Basics and working with Flows
Core concepts
Akka Streams is a library to process and transfer a sequence of elements using bounded buffer space. This latter property is what we refer to as boundedness and it is the defining feature of Akka Streams. Translated to everyday terms it is possible to express a chain (or as we see later, graphs) of processing entities, each executing independently (and possibly concurrently) from the others while only buffering a limited number of elements at any given time. This property of bounded buffers is one of the differences from the actor model, where each actor usually has an unbounded, or a bounded, but dropping mailbox. Akka Stream processing entities have bounded "mailboxes" that do not drop.
Before we move on, let's define some basic terminology which will be used throughout the entire documentation:
- Stream
- An active process that involves moving and transforming data.
- Element
- An element is the processing unit of streams. All operations transform and transfer elements from upstream to downstream. Buffer sizes are always expressed as number of elements independently form the actual size of the elements.
- Back-pressure
- A means of flow-control, a way for consumers of data to notify a producer about their current availability, effectively slowing down the upstream producer to match their consumption speeds. In the context of Akka Streams back-pressure is always understood as non-blocking and asynchronous.
- Non-Blocking
- Means that a certain operation does not hinder the progress of the calling thread, even if it takes long time to finish the requested operation.
- Graph
- A description of a stream processing topology, defining the pathways through which elements shall flow when the stream is running.
- Processing Stage
- The common name for all building blocks that build up a Graph. Examples of a processing stage would be operations like map(), filter(), custom GraphStage s and graph junctions like Merge or Broadcast. For the full list of built-in processing stages see Overview of built-in stages and their semantics
When we talk about asynchronous, non-blocking backpressure we mean that the processing stages available in Akka Streams will not use blocking calls but asynchronous message passing to exchange messages between each other, and they will use asynchronous means to slow down a fast producer, without blocking its thread. This is a thread-pool friendly design, since entities that need to wait (a fast producer waiting on a slow consumer) will not block the thread but can hand it back for further use to an underlying thread-pool.
Defining and running streams
Linear processing pipelines can be expressed in Akka Streams using the following core abstractions:
- Source
- A processing stage with exactly one output, emitting data elements whenever downstream processing stages are ready to receive them.
- Sink
- A processing stage with exactly one input, requesting and accepting data elements possibly slowing down the upstream producer of elements
- Flow
- A processing stage which has exactly one input and output, which connects its up- and downstreams by transforming the data elements flowing through it.
- RunnableGraph
- A Flow that has both ends "attached" to a Source and Sink respectively, and is ready to be run().
It is possible to attach a Flow to a Source resulting in a composite source, and it is also possible to prepend a Flow to a Sink to get a new sink. After a stream is properly terminated by having both a source and a sink, it will be represented by the RunnableGraph type, indicating that it is ready to be executed.
It is important to remember that even after constructing the RunnableGraph by connecting all the source, sink and different processing stages, no data will flow through it until it is materialized. Materialization is the process of allocating all resources needed to run the computation described by a Graph (in Akka Streams this will often involve starting up Actors). Thanks to Flows being simply a description of the processing pipeline they are immutable, thread-safe, and freely shareable, which means that it is for example safe to share and send them between actors, to have one actor prepare the work, and then have it be materialized at some completely different place in the code.
final Source<Integer, NotUsed> source =
Source.from(Arrays.asList(1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10));
// note that the Future is scala.concurrent.Future
final Sink<Integer, CompletionStage<Integer>> sink =
Sink.<Integer, Integer> fold(0, (aggr, next) -> aggr + next);
// connect the Source to the Sink, obtaining a RunnableFlow
final RunnableGraph<CompletionStage<Integer>> runnable =
source.toMat(sink, Keep.right());
// materialize the flow
final CompletionStage<Integer> sum = runnable.run(mat);
After running (materializing) the RunnableGraph we get a special container object, the MaterializedMap. Both sources and sinks are able to put specific objects into this map. Whether they put something in or not is implementation dependent. For example a FoldSink will make a CompletionStage available in this map which will represent the result of the folding process over the stream. In general, a stream can expose multiple materialized values, but it is quite common to be interested in only the value of the Source or the Sink in the stream. For this reason there is a convenience method called runWith() available for Sink, Source or Flow requiring, respectively, a supplied Source (in order to run a Sink), a Sink (in order to run a Source) or both a Source and a Sink (in order to run a Flow, since it has neither attached yet).
final Source<Integer, NotUsed> source =
Source.from(Arrays.asList(1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10));
final Sink<Integer, CompletionStage<Integer>> sink =
Sink.<Integer, Integer> fold(0, (aggr, next) -> aggr + next);
// materialize the flow, getting the Sinks materialized value
final CompletionStage<Integer> sum = source.runWith(sink, mat);
It is worth pointing out that since processing stages are immutable, connecting them returns a new processing stage, instead of modifying the existing instance, so while constructing long flows, remember to assign the new value to a variable or run it:
final Source<Integer, NotUsed> source =
Source.from(Arrays.asList(1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10));
source.map(x -> 0); // has no effect on source, since it's immutable
source.runWith(Sink.fold(0, (agg, next) -> agg + next), mat); // 55
// returns new Source<Integer>, with `map()` appended
final Source<Integer, NotUsed> zeroes = source.map(x -> 0);
final Sink<Integer, CompletionStage<Integer>> fold =
Sink.<Integer, Integer> fold(0, (agg, next) -> agg + next);
zeroes.runWith(fold, mat); // 0
Note
By default Akka Streams elements support exactly one downstream processing stage. Making fan-out (supporting multiple downstream processing stages) an explicit opt-in feature allows default stream elements to be less complex and more efficient. Also it allows for greater flexibility on how exactly to handle the multicast scenarios, by providing named fan-out elements such as broadcast (signals all down-stream elements) or balance (signals one of available down-stream elements).
In the above example we used the runWith method, which both materializes the stream and returns the materialized value of the given sink or source.
Since a stream can be materialized multiple times, the MaterializedMap returned is different for each materialization. In the example below we create two running materialized instance of the stream that we described in the runnable variable, and both materializations give us a different CompletionStage from the map even though we used the same sink to refer to the future:
// connect the Source to the Sink, obtaining a RunnableGraph
final Sink<Integer, CompletionStage<Integer>> sink =
Sink.<Integer, Integer> fold(0, (aggr, next) -> aggr + next);
final RunnableGraph<CompletionStage<Integer>> runnable =
Source.from(Arrays.asList(1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10)).toMat(sink, Keep.right());
// get the materialized value of the FoldSink
final CompletionStage<Integer> sum1 = runnable.run(mat);
final CompletionStage<Integer> sum2 = runnable.run(mat);
// sum1 and sum2 are different Futures!
Defining sources, sinks and flows
The objects Source and Sink define various ways to create sources and sinks of elements. The following examples show some of the most useful constructs (refer to the API documentation for more details):
// Create a source from an Iterable
List<Integer> list = new LinkedList<Integer>();
list.add(1);
list.add(2);
list.add(3);
Source.from(list);
// Create a source form a Future
Source.fromFuture(Futures.successful("Hello Streams!"));
// Create a source from a single element
Source.single("only one element");
// an empty source
Source.empty();
// Sink that folds over the stream and returns a Future
// of the final result in the MaterializedMap
Sink.fold(0, (Integer aggr, Integer next) -> aggr + next);
// Sink that returns a Future in the MaterializedMap,
// containing the first element of the stream
Sink.head();
// A Sink that consumes a stream without doing anything with the elements
Sink.ignore();
// A Sink that executes a side-effecting call for every element of the stream
Sink.foreach(System.out::println);
There are various ways to wire up different parts of a stream, the following examples show some of the available options:
// Explicitly creating and wiring up a Source, Sink and Flow
Source.from(Arrays.asList(1, 2, 3, 4))
.via(Flow.of(Integer.class).map(elem -> elem * 2))
.to(Sink.foreach(System.out::println));
// Starting from a Source
final Source<Integer, NotUsed> source = Source.from(Arrays.asList(1, 2, 3, 4))
.map(elem -> elem * 2);
source.to(Sink.foreach(System.out::println));
// Starting from a Sink
final Sink<Integer, NotUsed> sink = Flow.of(Integer.class)
.map(elem -> elem * 2).to(Sink.foreach(System.out::println));
Source.from(Arrays.asList(1, 2, 3, 4)).to(sink);
Illegal stream elements
In accordance to the Reactive Streams specification (Rule 2.13) Akka Streams do not allow null to be passed through the stream as an element. In case you want to model the concept of absence of a value we recommend using java.util.Optional which is available since Java 8.
Back-pressure explained
Akka Streams implement an asynchronous non-blocking back-pressure protocol standardised by the Reactive Streams specification, which Akka is a founding member of.
The user of the library does not have to write any explicit back-pressure handling code — it is built in and dealt with automatically by all of the provided Akka Streams processing stages. It is possible however to add explicit buffer stages with overflow strategies that can influence the behaviour of the stream. This is especially important in complex processing graphs which may even contain loops (which must be treated with very special care, as explained in Graph cycles, liveness and deadlocks).
The back pressure protocol is defined in terms of the number of elements a downstream Subscriber is able to receive and buffer, referred to as demand. The source of data, referred to as Publisher in Reactive Streams terminology and implemented as Source in Akka Streams, guarantees that it will never emit more elements than the received total demand for any given Subscriber.
Note
The Reactive Streams specification defines its protocol in terms of Publisher and Subscriber. These types are not meant to be user facing API, instead they serve as the low level building blocks for different Reactive Streams implementations.
Akka Streams implements these concepts as Source, Flow (referred to as Processor in Reactive Streams) and Sink without exposing the Reactive Streams interfaces directly. If you need to integrate with other Reactive Stream libraries read Integrating with Reactive Streams.
The mode in which Reactive Streams back-pressure works can be colloquially described as "dynamic push / pull mode", since it will switch between push and pull based back-pressure models depending on the downstream being able to cope with the upstream production rate or not.
To illustrate this further let us consider both problem situations and how the back-pressure protocol handles them:
Slow Publisher, fast Subscriber
This is the happy case of course – we do not need to slow down the Publisher in this case. However signalling rates are rarely constant and could change at any point in time, suddenly ending up in a situation where the Subscriber is now slower than the Publisher. In order to safeguard from these situations, the back-pressure protocol must still be enabled during such situations, however we do not want to pay a high penalty for this safety net being enabled.
The Reactive Streams protocol solves this by asynchronously signalling from the Subscriber to the Publisher Request(int n) signals. The protocol guarantees that the Publisher will never signal more elements than the signalled demand. Since the Subscriber however is currently faster, it will be signalling these Request messages at a higher rate (and possibly also batching together the demand - requesting multiple elements in one Request signal). This means that the Publisher should not ever have to wait (be back-pressured) with publishing its incoming elements.
As we can see, in this scenario we effectively operate in so called push-mode since the Publisher can continue producing elements as fast as it can, since the pending demand will be recovered just-in-time while it is emitting elements.
Fast Publisher, slow Subscriber
This is the case when back-pressuring the Publisher is required, because the Subscriber is not able to cope with the rate at which its upstream would like to emit data elements.
Since the Publisher is not allowed to signal more elements than the pending demand signalled by the Subscriber, it will have to abide to this back-pressure by applying one of the below strategies:
- not generate elements, if it is able to control their production rate,
- try buffering the elements in a bounded manner until more demand is signalled,
- drop elements until more demand is signalled,
- tear down the stream if unable to apply any of the above strategies.
As we can see, this scenario effectively means that the Subscriber will pull the elements from the Publisher – this mode of operation is referred to as pull-based back-pressure.
Stream Materialization
When constructing flows and graphs in Akka Streams think of them as preparing a blueprint, an execution plan. Stream materialization is the process of taking a stream description (the graph) and allocating all the necessary resources it needs in order to run. In the case of Akka Streams this often means starting up Actors which power the processing, but is not restricted to that—it could also mean opening files or socket connections etc.—depending on what the stream needs.
Materialization is triggered at so called "terminal operations". Most notably this includes the various forms of the run() and runWith() methods defined on Source or Flow elements as well as a small number of special syntactic sugars for running with well-known sinks, such as runForeach(el -> ...) (being an alias to runWith(Sink.foreach(el -> ...)).
Materialization is currently performed synchronously on the materializing thread. The actual stream processing is handled by actors started up during the streams materialization, which will be running on the thread pools they have been configured to run on - which defaults to the dispatcher set in MaterializationSettings while constructing the ActorMaterializer.
Note
Reusing instances of linear computation stages (Source, Sink, Flow) inside composite Graphs is legal, yet will materialize that stage multiple times.
Operator Fusion
Akka Streams 2.0 contains an initial version of stream operator fusion support. This means that the processing steps of a flow or stream graph can be executed within the same Actor and has three consequences:
- starting up a stream may take longer than before due to executing the fusion algorithm
- passing elements from one processing stage to the next is a lot faster between fused stages due to avoiding the asynchronous messaging overhead
- fused stream processing stages do no longer run in parallel to each other, meaning that only up to one CPU core is used for each fused part
The first point can be countered by pre-fusing and then reusing a stream blueprint as sketched below:
Flow<Integer, Integer, NotUsed> flow =
Flow.of(Integer.class).map(x -> x * 2).filter(x -> x > 500);
Graph<FlowShape<Integer, Integer>, NotUsed> fused =
akka.stream.Fusing.aggressive(flow);
Source.fromIterator(() -> Stream.iterate(0, x -> x + 1).iterator())
.via(fused)
.take(1000);
In order to balance the effects of the second and third bullet points you will have to insert asynchronous boundaries manually into your flows and graphs by way of adding Attributes.asyncBoundary using the method async on Source, Sink and Flow to pieces that shall communicate with the rest of the graph in an asynchronous fashion.
Source.range(1, 3)
.map(x -> x + 1).async()
.map(x -> x * 2)
.to(Sink.ignore());
In this example we create two regions within the flow which will be executed in one Actor each—assuming that adding and multiplying integers is an extremely costly operation this will lead to a performance gain since two CPUs can work on the tasks in parallel. It is important to note that asynchronous boundaries are not singular places within a flow where elements are passed asynchronously (as in other streaming libraries), but instead attributes always work by adding information to the flow graph that has been constructed up to this point:
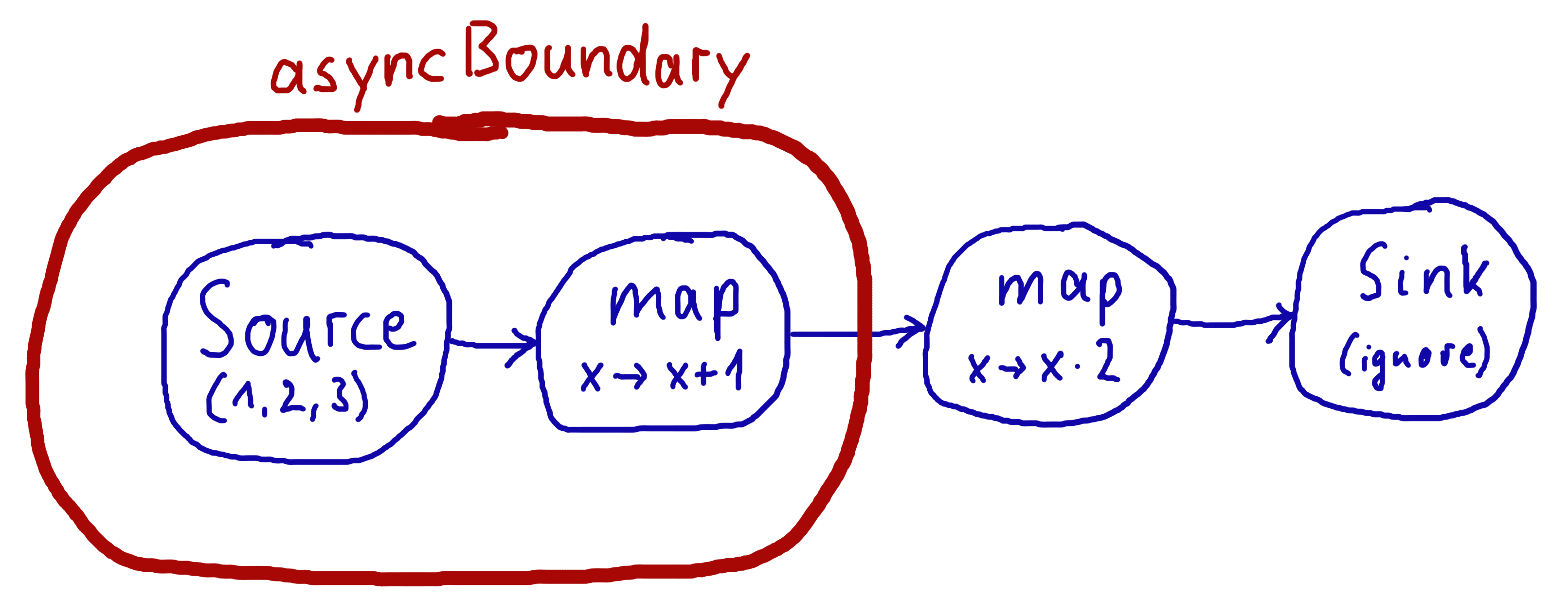
This means that everything that is inside the red bubble will be executed by one actor and everything outside of it by another. This scheme can be applied successively, always having one such boundary enclose the previous ones plus all processing stages that have been added since them.
Warning
Without fusing (i.e. up to version 2.0-M2) each stream processing stage had an implicit input buffer that holds a few elements for efficiency reasons. If your flow graphs contain cycles then these buffers may have been crucial in order to avoid deadlocks. With fusing these implicit buffers are no longer there, data elements are passed without buffering between fused stages. In those cases where buffering is needed in order to allow the stream to run at all, you will have to insert explicit buffers with the .buffer() combinator—typically a buffer of size 2 is enough to allow a feedback loop to function.
The new fusing behavior can be disabled by setting the configuration parameter akka.stream.materializer.auto-fusing=off. In that case you can still manually fuse those graphs which shall run on less Actors. With the exception of the SslTlsStage and the groupBy operator all built-in processing stages can be fused.
Combining materialized values
Since every processing stage in Akka Streams can provide a materialized value after being materialized, it is necessary to somehow express how these values should be composed to a final value when we plug these stages together. For this, many combinator methods have variants that take an additional argument, a function, that will be used to combine the resulting values. Some examples of using these combiners are illustrated in the example below.
// An empty source that can be shut down explicitly from the outside
Source<Integer, CompletableFuture<Optional<Integer>>> source = Source.<Integer>maybe();
// A flow that internally throttles elements to 1/second, and returns a Cancellable
// which can be used to shut down the stream
Flow<Integer, Integer, Cancellable> flow = throttler;
// A sink that returns the first element of a stream in the returned Future
Sink<Integer, CompletionStage<Integer>> sink = Sink.head();
// By default, the materialized value of the leftmost stage is preserved
RunnableGraph<CompletableFuture<Optional<Integer>>> r1 = source.via(flow).to(sink);
// Simple selection of materialized values by using Keep.right
RunnableGraph<Cancellable> r2 = source.viaMat(flow, Keep.right()).to(sink);
RunnableGraph<CompletionStage<Integer>> r3 = source.via(flow).toMat(sink, Keep.right());
// Using runWith will always give the materialized values of the stages added
// by runWith() itself
CompletionStage<Integer> r4 = source.via(flow).runWith(sink, mat);
CompletableFuture<Optional<Integer>> r5 = flow.to(sink).runWith(source, mat);
Pair<CompletableFuture<Optional<Integer>>, CompletionStage<Integer>> r6 = flow.runWith(source, sink, mat);
// Using more complex combinations
RunnableGraph<Pair<CompletableFuture<Optional<Integer>>, Cancellable>> r7 =
source.viaMat(flow, Keep.both()).to(sink);
RunnableGraph<Pair<CompletableFuture<Optional<Integer>>, CompletionStage<Integer>>> r8 =
source.via(flow).toMat(sink, Keep.both());
RunnableGraph<Pair<Pair<CompletableFuture<Optional<Integer>>, Cancellable>, CompletionStage<Integer>>> r9 =
source.viaMat(flow, Keep.both()).toMat(sink, Keep.both());
RunnableGraph<Pair<Cancellable, CompletionStage<Integer>>> r10 =
source.viaMat(flow, Keep.right()).toMat(sink, Keep.both());
// It is also possible to map over the materialized values. In r9 we had a
// doubly nested pair, but we want to flatten it out
RunnableGraph<Cancellable> r11 =
r9.mapMaterializedValue( (nestedTuple) -> {
CompletableFuture<Optional<Integer>> p = nestedTuple.first().first();
Cancellable c = nestedTuple.first().second();
CompletionStage<Integer> f = nestedTuple.second();
// Picking the Cancellable, but we could also construct a domain class here
return c;
});
Note
In Graphs it is possible to access the materialized value from inside the stream processing graph. For details see Accessing the materialized value inside the Graph.
Stream ordering
In Akka Streams almost all computation stages preserve input order of elements. This means that if inputs {IA1,IA2,...,IAn} "cause" outputs {OA1,OA2,...,OAk} and inputs {IB1,IB2,...,IBm} "cause" outputs {OB1,OB2,...,OBl} and all of IAi happened before all IBi then OAi happens before OBi.
This property is even uphold by async operations such as mapAsync, however an unordered version exists called mapAsyncUnordered which does not preserve this ordering.
However, in the case of Junctions which handle multiple input streams (e.g. Merge) the output order is, in general, not defined for elements arriving on different input ports. That is a merge-like operation may emit Ai before emitting Bi, and it is up to its internal logic to decide the order of emitted elements. Specialized elements such as Zip however do guarantee their outputs order, as each output element depends on all upstream elements having been signalled already – thus the ordering in the case of zipping is defined by this property.
If you find yourself in need of fine grained control over order of emitted elements in fan-in scenarios consider using MergePreferred or GraphStage – which gives you full control over how the merge is performed.
Contents